
Surfaces & Coatings-ANALYTICS IN THE AREA
Electrolytic Solutions and Process Baths
To apply high-quality and functional layers, coating baths must function flawlessly. We analyze the composition of metallic coating baths, pre- and post-treatments, and rinses using chemical and physical analytical methods. Due to the complexity of matrices and high salt concentrations, we have a large portfolio of analytical procedures available to precisely detect basic values, potential contaminants, and possible issues. We can also perform practical testing of electrolytes on a laboratory scale using the Hull cell method.

Electroplating solutions, coating baths, and rinses require constant monitoring. Important basic values must be maintained within their respective working ranges, and potential contaminants must not exceed certain tolerances. At the coating facility itself, continuous dosing is carried out. Whether the dosing amounts are correct, the degree of drag-out, and whether adjustments or dilutions are needed—all of this is part of process bath analysis. Using titration and instrumental analysis, we determine the overall condition of the coating baths and provide correction recommendations if necessary.
Foreign metals
Basic values of the baths
Surfactants and organic additives
Density, pH value, conductivity
Chromatographic analysis methods are used to analyze ionic or organic components in coating baths and electrolytes. Important components include sulfuric acid and catalysts in chrome baths, as well as brighteners in nickel and zinc electrolytes. We analyze the anionic components using ion chromatography (IC) and the organic components using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
Catalysts in hard chrome electrolytes
Sulfate in chrome baths
Brightener in nickel electrolytes
Anionic components in process baths

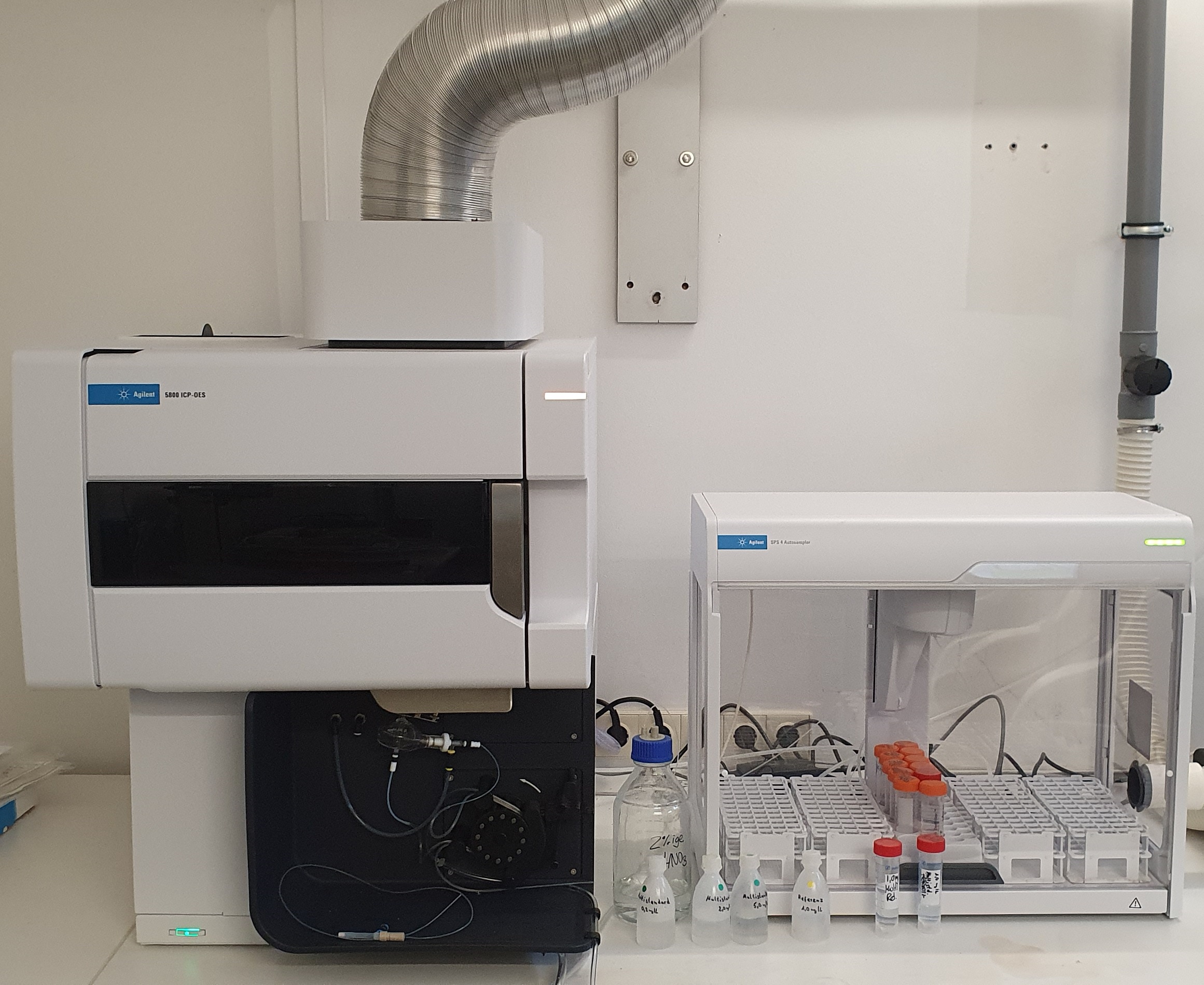
ICP-OES is an optical emission spectrometer with inductively coupled plasma. The bath sample is atomised in a suitable dilution in the plasma of the argon flame in the test device. The amount of the element to be determined in the sample is determined via the light absorption in the flame.
We can measure common metals with our ICP-OES. On the one hand, we have the ‘coating metals’, which are analysed in the clear two-digit gram range. On the other hand, foreign metals, i.e. contaminations carried over from other baths or from dissolving processes of the components to be coated, are an important indicator of the general condition of a coating bath.
What all measurements have in common is that we analyse in a very complex matrix with a high salt load.

Many of the basic values of coating baths can be analyzed by titration. For instance, the metal content of most electrolytes is titrated complexometrically, while acids or cyanides, hydroxides, and carbonates are analyzed by titration, as are chloride and boric acid, which can be reliably analyzed titrimetrically. Some analyses are performed manually using indicators for color change. Of course, we also have titration processors available. The variety of titration analytics is enormous—complexometric, iodometric, potentiometric, or as reversed titration, often with very complex preparations.
Physical parameters are crucial for the function of process baths and serve as good indicators for a trouble-free coating process. The advantage is that parameters like density, pH value, or conductivity can be determined relatively quickly and provide a rough indication of whether the bath parameters are within the tolerance range.
Tensiometry is somewhat more complex. We work with two different methods here: the ring tensiometer is used to measure static surface tension, while the bubble pressure tensiometer measures dynamic surface tension. The surface tension value can indicate the content of surfactants, which is an important parameter when it comes to uniform wetting of the surfaces to be coated.
pH value
Density and bath heaviness
Conductivity
Surfactants
Surface tension
For enquiries about these analyses, please contact our laboratory team at anfrage@industrial-lab.de or get in touch with your contact person:

Head of Team Process bath analysis
0212 22147 - 2
Send e-mail

Head of Laboratory
0212 22147 - 0
Send e-mail
Chromatography can be used to separate mixtures of substances into their individual components. Each substance has its own properties, which chromatography makes use of. The system of every chromatography consists of a mobile and a stationary phase. The mobile phase is the sample in combination with a running agent that “carries” the sample. The stationary phase separates the sample into its individual components. It consists of a gel or a solid that interacts with the mobile phase. Molecular interactions pull the sample mixture apart and the individual substances are detected in a chromatogram. This can be done directly on the stationary phase by means of differently pronounced running lines or spreading or via a detector.
HPLC stands for high pressure liquid chromatography. HPLC is used to detect and quantify organic components of a liquid sample. The sample with a suitable solvent is the mobile phase, which is passed over a stationary phase. The stationary phase is packed in a column and consists of silica gel with the addition of oxides, cellulose or polymers of different grain size, shape and size, which in turn represent functional groups. The mobile phase is passed over the column with the stationary phase and the components to be detected remain attached to the functional groups of the stationary phase. The column therefore separates the mixture. Depending on the substance, the dwell times at the “capture points” of the column vary, which are used for evaluation on the detector.